
Specifically, this invention is a method for creating a flipbook using a video camera, a computer running a computer program, a printer, a business card slitter, and a stapler. The present invention is thus directed towards a method for creating a flipbook inexpensively and quickly using standard, readily available equipment. A need therefore exists for a method of quickly and easily creating flipbooks using standard, readily available equipment SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Consequently, flipbook images in the prior art are created by printing images sequentially, one by one, on non-standard sizes of paper (usually much smaller than standard 8.5 inch by 11 inch paper) using specialized printing equipment, which drives up the cost. The flipping pages create the illusion of motion by causing each image to be visible to the user for a short period of time and quickly replacing it with the next image.Īlthough viewed without using bulky equipment or electricity, flipbooks are limited by the maximum page size that allows the pages to flip fast enough to recreate motion. A flipbook is a book that has sequential images contained on each successive page such that when the pages are flipped by a user in rapid succession from the first page to the last page, it creates the illusion of motion. By contrast, an animated book, or flipbook, can display video footage without any special bulky equipment or electricity. One of the drawbacks to reproducing video footage using a projector, television or computer monitor is that such reproduction typically requires bulky, specialized equipment and electricity. Like photographs, video is primarily used as a means of communication between people.
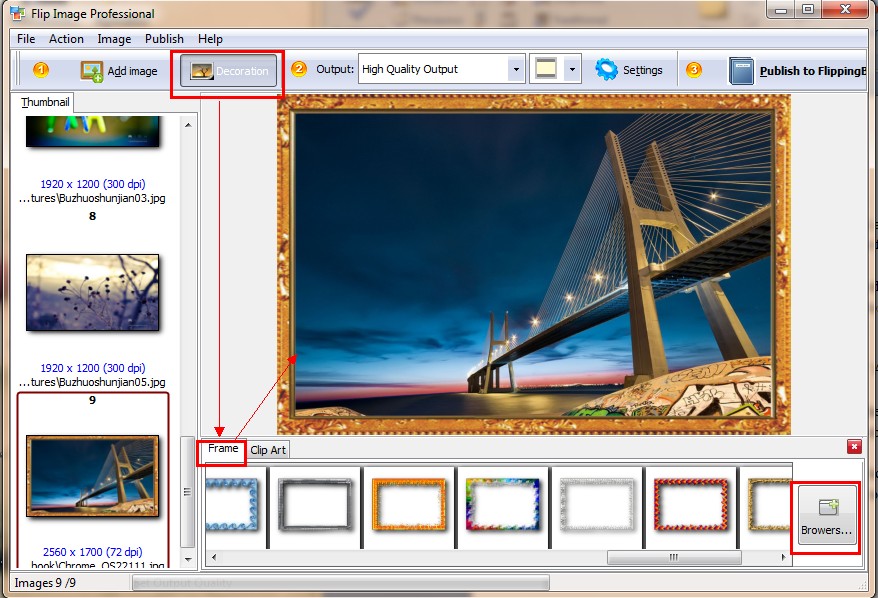
Video footage can be captured or recorded on film or digital media, and is typically played back using a projector, television, or computer monitor. Video footage can be characterized according to its frame rate, which is the number of still images captured or shown per unit of time.
Flipbook how to add frames series#
Video is a technology that captures a series of sequential images over a period of time, and reproduces the images in the same order they were captured to simulate motion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
